Study on the brightness of tunneling objects based on light climate theory
1 Introduction
Highway tunnels are special structures on highways, and lighting has its own particularity. During the daytime, the brightness outside the tunnel is very high. When the driver enters the dark tunnel from the high-brightness tunnel, due to the visual adaptation characteristics of the human eye, a certain adaptation time is required. In order to avoid the safety problems that may occur due to visual adaptation, high illumination brightness is needed in the entrance and transition sections of the tunnel to ensure a smooth transition of visual adaptation and ensure driving safety. However, high inlet and transition brightness means high power consumption and maintenance costs.
In the tunnel lighting design standards or guidelines of various countries, the brightness value of the tunnel entrance section is based on the “outside hole average brightness value L20(S) in the field of view of a parking line of sightâ€, multiplied by the brightness reduction factor k. Calculated. Therefore, the design reference of tunnel lighting—the value of the outside brightness of the hole L20(S) will directly affect the brightness of the inlet section and the transition section, and also determines the tunnel lighting energy saving, operating cost and driving safety.
The brightness value L20(S) of tunnel tunnels as the most basic parameter of tunnel lighting design has been studied by researchers in many countries. Based on these studies, the recommended values ​​for the brightness of the tunnel cavity are given. The recommended values ​​for CIE and the EU for the brightness outside the tunnel are based on Postma's relevant records on daylight in the Netherlands. The UK's tunnel lighting standards for the regulation of the brightness outside the hole are based on Hunt's (1979) study of the frequency status of daylight illuminance at any time of the year. The external brightness value of the hole in the Japanese Tunnel Lighting Standard (JIS Z 9116-1990) is measured by Yoshikawa et al. for a typical highway tunnel in the central mountainous area of ​​Japan for one year, giving the average brightness outside the hole.
China's research on tunnel lighting started late, and the experience and basic work were insufficient. The theoretical research is basically blank. The currently used "Tunnel Ventilation Lighting Design Specification (JTJ026. 1-1999)" is a direct reference to the CIE tunnel lighting guidelines and EU tunnel lighting standards. There is neither long-term observation data based on it, nor the actual light and climatic conditions and regional differences in China.
In order to fill this gap, in the late 1990s, the Chongqing Academy of Transportation Science conducted a measurement of the brightness outside the hole in Fujian through the environmental sketch method. In October 2001, the Shanghai Institute of Lighting and Lighting used the blackness method to test the tunnel entrance brightness of 10 tunnels in Fujian. From 2005 to 2006, Chongqing Transportation Research Institute used the digital camera on-site photo method to test and analyze the external brightness data of 32 tunnel openings in several highway sections of Fujian Province. However, since the test is limited to the province of Fujian, and the light environmental conditions in each tunnel test are highly random, it is impossible to express the difference in brightness outside the hole in different regions and different light and climatic conditions.
In order to obtain the brightness of the tunnel tunnel in different areas, it is necessary to test the brightness of the tunnel outside the tunnel in a large scale and for a long time, and it is possible to obtain representative and suitable brightness parameters in a certain area. At present, there is no such large amount of long-term hole brightness test data as the basis for setting standards. In fact, different geographical locations, different light and climatic conditions, and different materials and reflection properties of the hole elements have large differences in surface brightness values. China has a vast territory, a large geographical latitude span, and huge differences in light and climatic conditions. It is not rigorous to use local data as a national industry standard and norm.
Therefore, in order to obtain the brightness values ​​of tunnels and external scenes that are in line with China's national conditions and reflect different light and climate differences in different regions, this paper proposes to use existing long-term observations of light and climate data based on light climate theory. To study the brightness of the tunneling scene. This kind of research method can make up for the insufficiency of the observation data and theoretical research of the brightness of the external scenery of the cave in China, and can also compensate for the accidental error caused by the random measurement.
2 Reference light climatic conditions of the brightness of the tunnel tunnel
In order to ensure the traffic safety of the tunnel entrance section under any circumstances, in principle, the entrance section brightness (Lth) needs to be designed to be the highest inlet section brightness value that may occur throughout the year, that is, to take the maximum surface brightness value of the year-round cave scene. Value basis. However, in the actual tunnel lighting design, if the brightness value of the entrance section is calculated by the brightness value of the surface of the largest hole in the whole year, high inlet section illumination is required, regardless of the economics of lighting or the necessity of engineering implementation. Sex is not appropriate.
The International Commission on Illumination clearly states in document CIE 88-2004: “If the brightness of the entrance section is calculated using the highest brightness value appearing on the surface within the field of view, high inlet section illumination will be required. Therefore, it is proposed to appear at least 75 in a year. The highest brightness value of the hour is used as the calculation reference value..." This formulation is actually based on the concept of cumulative frequency. What is proposed in the CIE standard is not directly at the highest value for a particular time, but rather a larger value than a certain frequency of occurrence.
Based on the above point of view, starting from the actual needs of the project, the maximum brightness value of the cumulative appearance frequency of 75 hours is used as the standard reference value for determining the surface brightness of the cave exterior. Therefore, this paper determines the light climatic conditions corresponding to the maximum brightness value of the cumulative frequency of 75 hours as the reference reference climatic conditions for studying the brightness of tunneling objects.
This paper uses the climatic observation data of the light climate observatory stations of 14 representative cities across the country, organized by the Chinese Academy of Meteorological Sciences and the China Academy of Building Research from 1983 to 1984, including: Illumination, horizontal illuminance, horizontal illuminance, and observations of surface conditions and cloud conditions are based on observations.
Firstly, taking Chongqing as an example, through the screening and analysis of the total illumination of the water level recorded in Chongqing in 1984, it was found that the total illumination of the maximum horizontal plane in Chongqing in 1984 was 125000lx, which appeared at 12:30 on August 15, 1984.
The maximum horizontal illumination value with a cumulative frequency of 75 hours is 97000lx, ie: 75 hours of total horizontal illumination in the year-round recorded data is greater than 97000lx, see Figure 1.
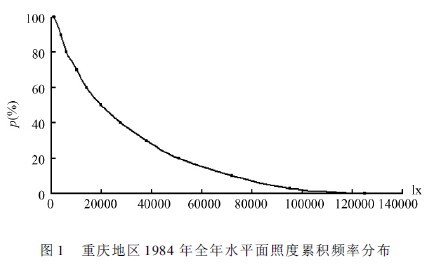
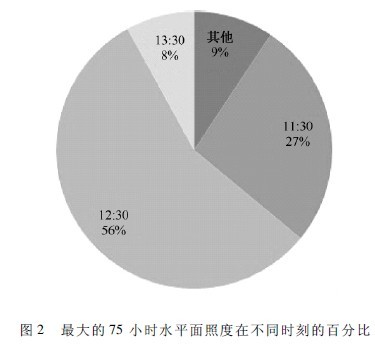
Analyze the ratio of 75-hour horizontal illumination values ​​greater than 97000lx at different times and in different months, as shown in Figures 2 and 3. It can be seen from Figure 2 that the maximum 75 illuminance values ​​appear mainly around noon. Appeared at 12:30 and 11:30 for a total of 83%; appeared in other time periods: 6 at 10:30 and 1 at 14:30.
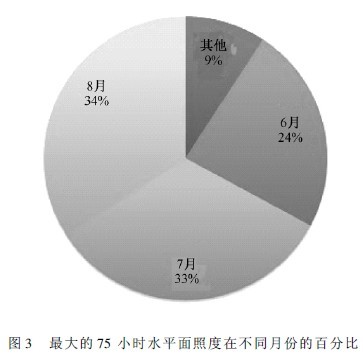
If you consider the seasonal distribution of the maximum 75 illuminance values, you can see from Figure 3 that all are in the warm half season. In June, July and August, it accounted for 91%, and the other 9% appeared in May and September. And the proportions appearing in June, July and August are relatively close, and are distributed approximately evenly in the summer of 3 months.
Cumulative appearance frequency reaches 75 hours of horizontal illuminance, that is, 75 maximum horizontal illuminance values ​​greater than 97000lx, and the corresponding solar conditions are visible to the sun, 80% of which is θ2 and 20% of θ is θ . There is no case where the day is П. This means: The maximum value of the water illuminance appears in the sunny state.
Based on the above analysis, the external brightness of the tunnel in Chongqing can be used to define the reference reference climatic conditions as: Sunny day at noon on the summer solstice, and the reference solar illuminance can be selected as 97000lx.
Further analysis of the light climate observation data of 13 other cities, the same conclusion is reached: The maximum horizontal illumination value of the cumulative frequency of 75 hours appears in the sunny day before and after the summer noon. It is only the maximum horizontal illumination value with a cumulative frequency of 75 hours, and there are differences in different regions.
Therefore, it is appropriate to use the maximum horizontal illuminance with a cumulative appearance frequency of 75 hours and the corresponding sky conditions as the reference reference climatic conditions for calculating the brightness of the tunnel tunnel exterior. The difference in light climate between different regions is reflected in the difference in the magnitude of the reference water level.
3 Reference surface illuminance of tunnel tunnels under light and climatic conditions
Through field research on more than 20 tunnels in Chongqing, Guizhou, Fujian and other places, it is found that within the tunnel sight area and 20° field of view outside the tunnel, typical scene elements include openings, pavements, end walls, slope protection, rock walls, Greenery, buildings, billboards, etc. The brightness of these illuminated surfaces depends on the illuminance value and reflection characteristics of the illuminated surface. There was no sky in the tunnel under investigation, so the sky brightness was not considered in the discussion in this article.
3. 1 Conversion factor between horizontal illuminance value and vertical illuminance value
For the surface of the tunnel hole, except for the road surface, which is usually a horizontal plane, the other surface is either an inclined surface or a vertical surface. Generally, tunnel end walls, billboards, and buildings are vertical or near-vertical, while rock slopes and greening are usually inclined. Due to the relative positional relationship with the line of sight, the turf and the slope wall can be considered as vertical planes perpendicular to the line of sight in the micro-unit. This simplifies the calculation of the brightness of the surface of the tunnel entrance.
Since all the surface of the tunnel entrance can be simplified to the vertical plane, if the conversion relationship between the horizontal illumination and the vertical illumination can be found, the horizontal illumination value in the light climate observation data can be conveniently converted into the vertical illumination.
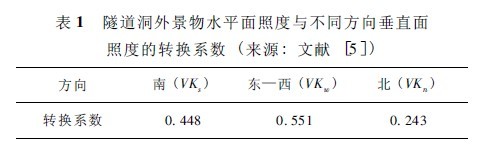
The vertical illuminance conversion coefficient refers to the ratio of the illuminance of a vertical plane to the total illuminance of the horizontal plane under a standard sky. Dr. Yu Yucheng from Chongqing University conducted research on this and gave the vertical illuminance conversion coefficients of different orientations related to the surface condition and cloud cover. Corresponding to the reference sky condition for studying the brightness of the external view of the tunnel mouth, in order to simplify the calculation, we select the standard sunny sky condition, that is, the vertical illuminance conversion in different directions under the condition that the solar condition is θ2 and the total cloud amount is 0. coefficient. Since the reference light climatic conditions for studying the brightness of the tunnel cavity are the noon on the summer solstice, and the vertical illuminance conversion coefficient in the east-west direction at noon time should be basically the same, therefore, according to the literature [5], the east-west direction is combined and averaged. The value gives the vertical illuminance conversion factor under reference sky conditions for the maximum horizontal illuminance of the cumulative appearance frequency of 75 hours, as shown in Table 1.
3. 2 Taking Chongqing as an example to calculate the surface illumination of the tunnel tunnel
Based on the study of light climate theory and the use of existing results, as well as the analysis of existing light climate observation data in Chongqing, we determined that the reference water level illumination outside the tunnel tunnel in Chongqing is 97000lx, and the reference sky condition is the summer solstice noon standard. It is empty on sunny days. According to the vertical illuminance conversion coefficient table (Table 1) selected according to this condition, the surface illuminance values ​​of different orientations are calculated, as shown in Table 2. For the sake of simplicity and at the same time meet the needs of the project, accurate to 1000lx.
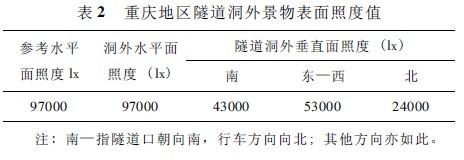
4 Surface brightness of typical scenes outside the tunnel
Usually for driving safety, the building at the entrance of the tunnel tries to avoid using materials with high directional reflectivity. Therefore, we define the typical scene surface outside the tunnel as a diffuse or nearly diffuse surface. For uniform diffuse reflection, it can be calculated by the formula: L = EÂ·Ï /Ï€.
In order to simplify the calculation, this paper divides the typical tunnel hole exterior elements into several categories, considering their surface brightness.
a) Hole brightness: According to the brightness requirement of the entrance section of the tunnel, the brightness of the hole is directly given as 200cd / m2. Discussions were made on pavements, structures and green vegetation.
b) Road surface brightness: The road surface is special, the surface is water level, and the reflection characteristics are special due to the different materials of the road surface and the pollution during use. Inspect the surface brightness of the pavement, first determine the reference water illuminance of a certain area, and the direct illuminance and scattering illuminance of the reference water illuminance; determine the zenith angle γ of the sun at noon on the summer solstice in the region; according to the solar zenith angle and pavement material practices Determine the type of pavement. Check the simplified brightness coefficient table of CIE to determine the brightness coefficient r under the sky condition and the road condition, and obtain the brightness of the direct sunlight. The average reflection coefficient Q0 of the scattered light is determined according to the road material, and the brightness of the scattered light is calculated, and the sum of the two is the road surface brightness under natural light conditions.
c) the surface brightness of the building: first assume that it is a uniform diffuse or nearly uniform diffuse material; according to the reference plane climatic conditions, the vertical plane conversion coefficient of the reference plane illuminance is converted into vertical illuminance in different directions, according to common material reflection The coefficient of the selected material in the coefficient table allows you to calculate the surface brightness of the building. In order to simplify the calculation, this paper is divided into dark and light materials, and two typical reflection coefficient values ​​(Ï = 0.2 and Ï = 0.5) are calculated.
d) Vegetation greening surface brightness: The shrubs, trees and herbaceous plants on the slope are understood as vertical planes; the vertical plane conversion coefficients of the reference horizontal illumination are converted into vertical illumination in different directions. By selecting two different shades of vegetation (Ï = 0.05 and Ï = 0.1), the surface brightness of the vegetation can be calculated.
The simplified values ​​of the typical scenes outside the tunnel in Chongqing after the simplification are shown in Table 3.
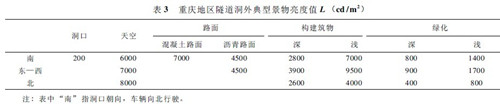
Similarly, the reference light climatic conditions can be determined according to the light climate observation data of different regions, and the surface brightness of typical scenes outside the tunnel hole in each region can be calculated as the benchmark parameters and basis for the tunnel lighting design.
5 Summary
Based on the research results of tunnel lighting at home and abroad, based on the theory of light climate, combined with the concept of CIE on the cumulative frequency of the value of the external brightness value of tunnel tunnel, this paper determines the reference light climatic conditions as the calculation of the brightness of the tunnel cavity. Benchmark. The universality of this theory is studied by analyzing the light climate observation data of several cities. Taking Chongqing as an example, the method of calculating the brightness value of the typical scene outside the tunnel is given, and the brightness value of the typical scene outside the tunnel is calculated.
The light climate theory studies the brightness of the tunnel tunnel external scenery, and can obtain the standard reference value of the brightness of the tunnel tunnel externally more accurately and more in line with the characteristics of China's light climate, and provide more realistic basic data for the tunnel lighting design to avoid the brightness outside the tunnel hole. Energy insufficiency due to inaccurate value or potential safety hazard.
Tom Spa will create an upscale atmosphere with its sophistication and contemporary design. The grey and white hues have a timeless style that will keep your salon on trend through all four seasons. Each piece in this collection is crafted with real, high quality wood and lab marble that are acetone and scratch resistant.

Manicure Table,Manicure Bar Table,Luxury Manicure Tables,Folding Manicure Table
TOM SPA BEAUTY SALON EQUIPMENT CO.,LTD , https://www.tomspabeauty.com