About the type and production method of low frequency traps
[Home Theater Network HDAV.com.cn] First, what is a low frequency trap?
The low frequency trap is a sound absorbing structure specially designed to absorb specific low frequency standing waves. It is a special acoustic processing device installed in the corner. The low frequency trap is a product specially designed for home theaters and listening rooms. It improves the low frequency low frequency response, eliminates or delays standing waves, and makes the sound clearer, thus improving the sound system quality. The diameter of the low frequency trap determines its lower limit of absorption frequency. The low-frequency trap is the main sound-absorbing device that controls the low-frequency absorption in the corner of the room. The lower limit of absorption is 40HZ or lower, and the diffusion is above 400HZ. The top layer is a high-grade breathable faux leather fabric. The material is composed of four centrifuge cylinders of different diameters. The low-frequency traps are divided into two types: fan-shaped and cylindrical. The fan-shaped trap can be fixed at the corner of the corner, and the cylindrical low-frequency trap can be placed at a corner of the wall at random, without fixing. Easy to install, change layout at any time, can be placed directly in the corner, or can be mounted by some auxiliary hanging accessories.

Second, the type of low frequency trap
There are several types of low frequency traps that are common, each with some small variants.
Helmholtz resonator
The Helmholtz resonator is named after the authoritative scientist Herman von Helmholtz (1821-1894) in this field. Its design principle is simple, a large box with a small opening will resonate with a specific frequency. Think about what sound it makes when you blow along the soda bottle, and you'll be inspired. Any sound waves falling into the low frequency trap band will cause the air inside the box to reciprocate. The sonic energy is then consumed into the air (in the tank) to remove the sonic energy in the room. This is an idealized state, but close enough to our intentions. The Helmholtz resonator can be designed as a narrow band (only problematic frequencies are removed) or as a wide band for a frequency domain. However, it requires that the cabinet must be hard and heavy. Because it is usually too bulky and difficult to construct.

Resonant low frequency trap
The resonant low frequency trap uses a sound absorbing material, which is commonly referred to as a panel trap. It usually consists of a thin splint or similar material. Panel traps typically use fiberglass to broaden the absorption range, and when designed well, it can effectively cover an octave. Although still not perfect, it has a wider range of absorption than the Helmholtz trap. When such a trap is used to process a room, another type is usually used, one for controlling frequencies around 100 hz and the other for 200 hz. This is acceptable in the main frequency band of low frequency 80-300hz (translation may be wrong). Although such traps are not as cumbersome as the Helmholtz-style traps, they are still small and often expensive, requiring complex and careful analysis.
Glass fiber broadband absorption
Rigid fiberglass is similar to household fluff, which can be compressed to a quarter of its original volume and stuffed into panels one to four inches thick. A three inch thick panel that is inserted into fiberglass has a sound absorbing performance equivalent to an uncompressed one foot thick glass fiber. The biggest advantage of low-frequency traps using fiberglass is that it is suitable for a wider range of frequencies because it is not based on the principle of resonance. Hard fiberglass panels are also used in large quantities to absorb medium to high frequencies. High performance can be achieved by combining a hard glass fiber membrane. Like this hybrid design can cover a wide range of frequencies, low frequency can dive to 80hz or even lower. Traps using glass fibers are difficult to produce sufficient effective absorption for frequencies below 80 hz. However, most rooms do not need to absorb frequencies below 80hz. Because sheet rock walls penetrate and absorb these extremely low frequencies. So unless you have a wall made of cement or brick, or a cavity separated by two stone walls, a fiberglass trap is the best choice.
Other types
In addition to the aforementioned, Helmholtz resonators, panel traps, fiberglass traps, as well as diaphragm material absorbers and wood veneer bass traps.
Method of adjusting low frequency effects
It is also possible to obtain a better curve from the phase cut by adjusting the equalizer, but in fact, this method cannot fundamentally solve the standing wave and sound wave interference.
Adjusting the speakers, adjusting the listening position, and setting the low-frequency traps are all ways to alleviate standing waves and sonic interference, but these are caused by the actual defects in the room.
Absorbent panels for handling medium to high frequencies are typically very thin and can be placed flat on a wall or ceiling. Low-frequency traps are usually very large, at least very thick, and they generally work best near the corner. Placing too much medium and high frequency absorbing material can cause the sound to dry up and lack of energy. But it doesn't matter for the low frequency. The more low-frequency traps, the deeper the low-frequency will be, and the flatter the low-frequency frequency curve will be.
Third, the steps to make a bass trap:
First of all, the materials you need. Below is a list: 2 1" X3" edging strips (24" X48"); liquid nails for adhesive spraying; 1.5 staple burlap fabric heavy duty stapler; 250 1/2 "work gloves 2"; fiberglass circuit board (24"X48") ​​(x2 of the bass trap).
Glue liquid staples bind the edging strips together to create a frame bass trap.
For bass traps, glue two, plate adhesive spray. For normal sound absorbing panels, you can skip this step.
The adhesive glue spray frame used.
The canvas is on the floor and the frame is bound. The binding is rich, ensuring tightness on the canvas.
Use the adhesive to spray the burlap fabric, the bass trap on the back.
In this way, the bass trap is complete.
It is now more popular to use wooden panels, or wooden strips to frame, and then fill the glass wool, which is what we often call soundproof cotton, sound-absorbing cotton. The density and thickness of the sound absorbing cotton determine the frequency of the low frequency absorbed, that is, the thicker and denser the density, the lower the bass frequency absorbed.
Several common bass traps are shown in the following figure:
Cylinder low frequency trap
Easy to do
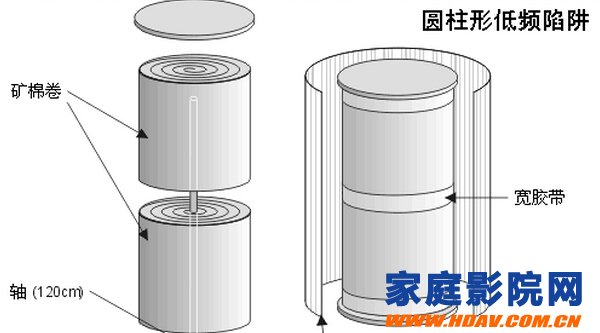
The picture above is cylindrical
Flat low frequency sound absorber
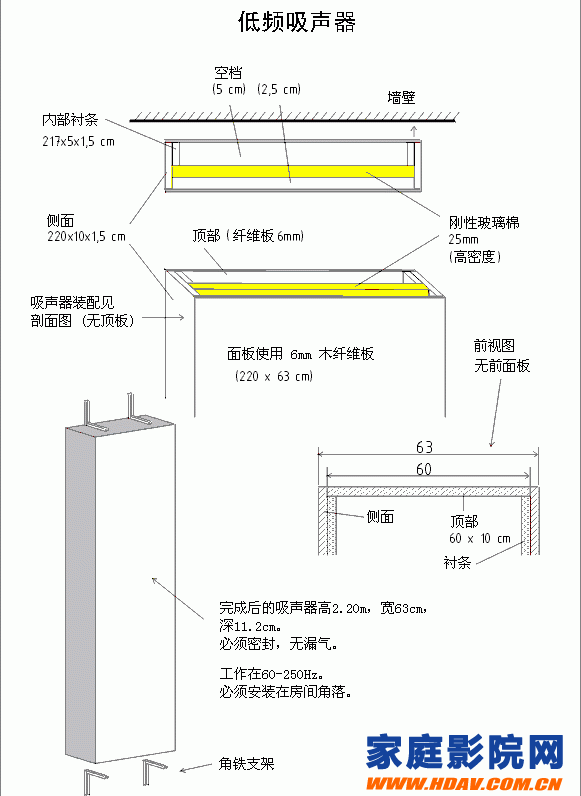
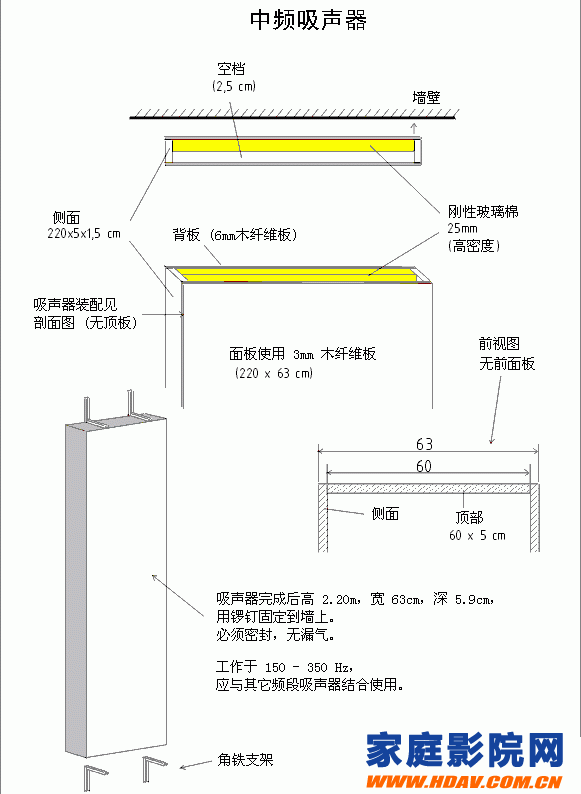
Intermediate frequency sound absorber
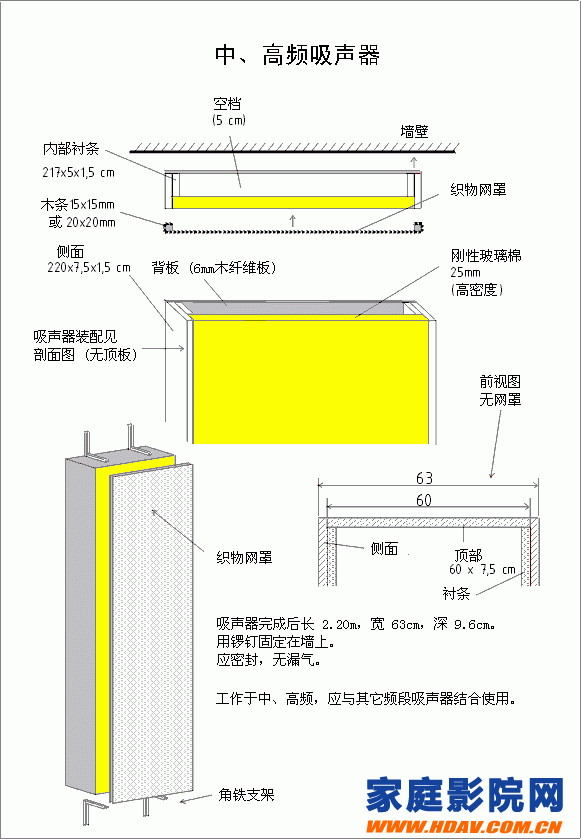
Medium and high frequency sound absorber
The sound absorption characteristics of the medium and high frequency sound absorber (total thickness 5 cm) are made of 4 mm fiberboard.
frequency
125 250 500 1k 2k 4K
No sound absorption cotton 0,30 0,36 0,20 0,19 0,12 0,05
There are sound-absorbing cotton 0,40 0,50 0,40 0,24 0,14 0,05
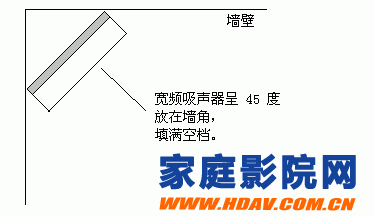
Broadband sound absorber
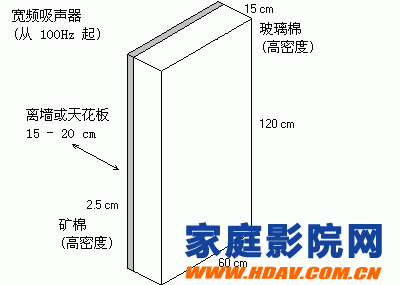
Broadband in the corner has the best effect
The small compartment is filled with 25mm thick sound absorbing cotton.
Resonance frequency calculation: Fr = 508 x [SQRT (P / de)]
Here P = perforation rate
d = box depth, cm
e = panel thickness + 0.8 aperture, cm
The perforation rate is calculated as: P=78.5(d/D)^2
Where D = hole center distance, mm
d = hole diameter, mm
|--D--|
--OO
|
D
|
--O ->O<-d
After filling in the sound-absorbing cotton, it will affect the theoretical calculation.
The table below is a typical sound absorption performance. Three different perforation rates were used: 0.5% (low frequency absorption), 5% (low frequency absorption), 25% or more (wide frequency). In the last row, the box is only 5cm deep, the panel has a 6mm thick perforation rate of 0.5%, and is filled with 50mm high-density glass wool or rock wool.
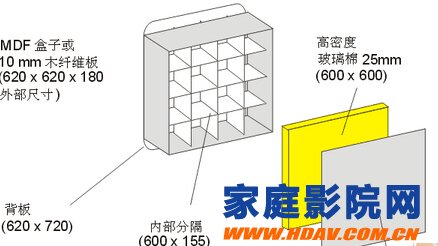
The picture above shows the box type
Triangular low frequency trap
The two traps are stacked, and the sound absorption for 80-100Hz is quite good, and it can reach 1 Sabin (100%). Below this frequency (about one octave lower) works better, but the calculation is difficult.
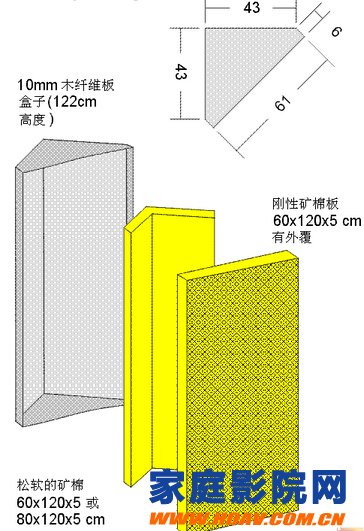
The picture above is a triangle
Corner film sound absorber
Another triangle trap. Use wood fiberboard as a panel to reflect more sound waves and only absorb low frequencies.
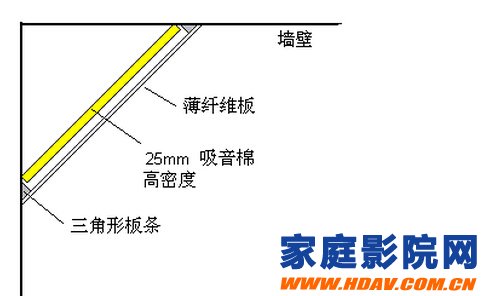
The picture above is another triangle
In general low frequency traps, we can put the bass in the corner to prevent low frequency standing waves. There are subtle differences in the frequency bands that these models are designed for, and the specific conditions can be used together.
Above we introduced some basic knowledge of low frequency traps. For the detailed placement method of low frequency traps, please see the "Low Frequency Trap Placement Method" here.
More fresh and fun home theater information, please pay attention to home theater network http:// (WeChat: cnhifi), the country's most influential home theater audio player interactive media website.
Electric Equipment Cable,Pvc Control,Aircraft Control Cable,Electric Guitar Lead
HENAN QIFAN ELECTRIC CO., LTD. , https://www.hnqifancable.com