The maximum transmission distance of twisted pair cables in network data communication is famously capped at 100 meters. Whether it's Category 3, Category 5, or even Category 6 cabling, all are limited to this distance for reliable performance. This limit is not arbitrary—it’s rooted in the physics of signal transmission and the design principles of Ethernet networks.
In the structured wiring standards, horizontal cabling is restricted to a maximum of 90 meters, while the total link length cannot exceed 100 meters. This 100-meter limit applies from the network card to the hub or switch. But why exactly is this the case? The answer lies in the way signals propagate through copper wires.
As an electrical signal travels along the twisted pair, it encounters resistance and capacitance, which cause signal attenuation and distortion. These factors reduce the quality of the transmitted data, making it harder for the receiving device to interpret the information correctly. To maintain stable and accurate communication, there must be a practical limit on how far a signal can travel without degrading beyond acceptable levels.
This brings us to the concept of "bit time." For a 100 Mbps Ethernet connection, each bit takes about 10 nanoseconds to transmit. In order for the Ethernet protocol (CSMA/CD) to function properly, a device must detect a collision before the entire frame is sent. The minimum Ethernet frame size is 64 bytes, or 512 bits, which takes 5,120 nanoseconds to transmit. During this time, the signal must still be detectable across the entire cable length.
The delay caused by the cable itself is also a factor. For example, Category 5 UTP has a delay of approximately 5.56 nanoseconds per meter. When you add up the delays from all components in the network, including switches, hubs, and other devices, the total must not exceed the 5,120 nanoseconds allowed by the protocol. This calculation leads to the 100-meter limit.
If the cable exceeds this distance, the collision detection mechanism may fail, leading to packet loss and retransmissions. While shorter distances may allow for some flexibility, especially at lower speeds like 10 Mbps, exceeding 100 meters is generally not recommended. Even if the network appears to work initially, long-term reliability issues may arise, such as intermittent connectivity or performance degradation.
When using Power over Ethernet (PoE), the same 100-meter rule applies. Although PoE delivers power along with data, the physical limitations of the cable remain. Some installers may push the limits for cost savings, but this can lead to voltage drops and reduced efficiency. To ensure optimal performance, it's best to stick to the 80–90 meter range in real-world installations.
Cable quality also plays a significant role. Lower-quality cables, especially those made with cheaper materials like copper-clad iron or steel, can significantly reduce the effective transmission distance. These substandard cables may pass initial tests but can cause network instability, packet loss, and other issues over time.
Category 5e cables improve upon standard Category 5 by reducing crosstalk and improving overall performance, making them ideal for Gigabit Ethernet. Category 6 cables offer even better performance, supporting higher frequencies and greater bandwidth, though their maximum transmission distance remains around 100 meters under standard conditions.
Ultimately, while modern cabling may sometimes exceed the 100-meter limit in practice, doing so risks future compatibility and reliability. As network speeds continue to increase, adhering to these guidelines becomes even more critical. Always use high-quality cables and follow industry standards to ensure a stable and scalable network infrastructure.
Solar Engergy System
Solar energy system, off gird pv system, grid pv system, solar power system, Solar Panel system, on grid solar system, grid tied solar system,20kw solar system
Solar energy system include Solar photovoltaic system: 1. Off grid photovoltaic system mainly consists of solar modules, controllers, and batteries. To supply power to AC loads, it is also necessary to configure an AC inverter. 2. Grid connected photovoltaic power generation system. 3. Distributed photovoltaic power generation system. Distributed power generation or distributed energy supply.
|
solar cell type
|
mono crystalline, half cut cell
|
|
solar energy pv system include
|
on grid system, off grid system, hybrid system
|
|
solar configuration
|
solar panel, inverter, battery, bracket cabels, mc4 connector
|
|
|
Product details and pic
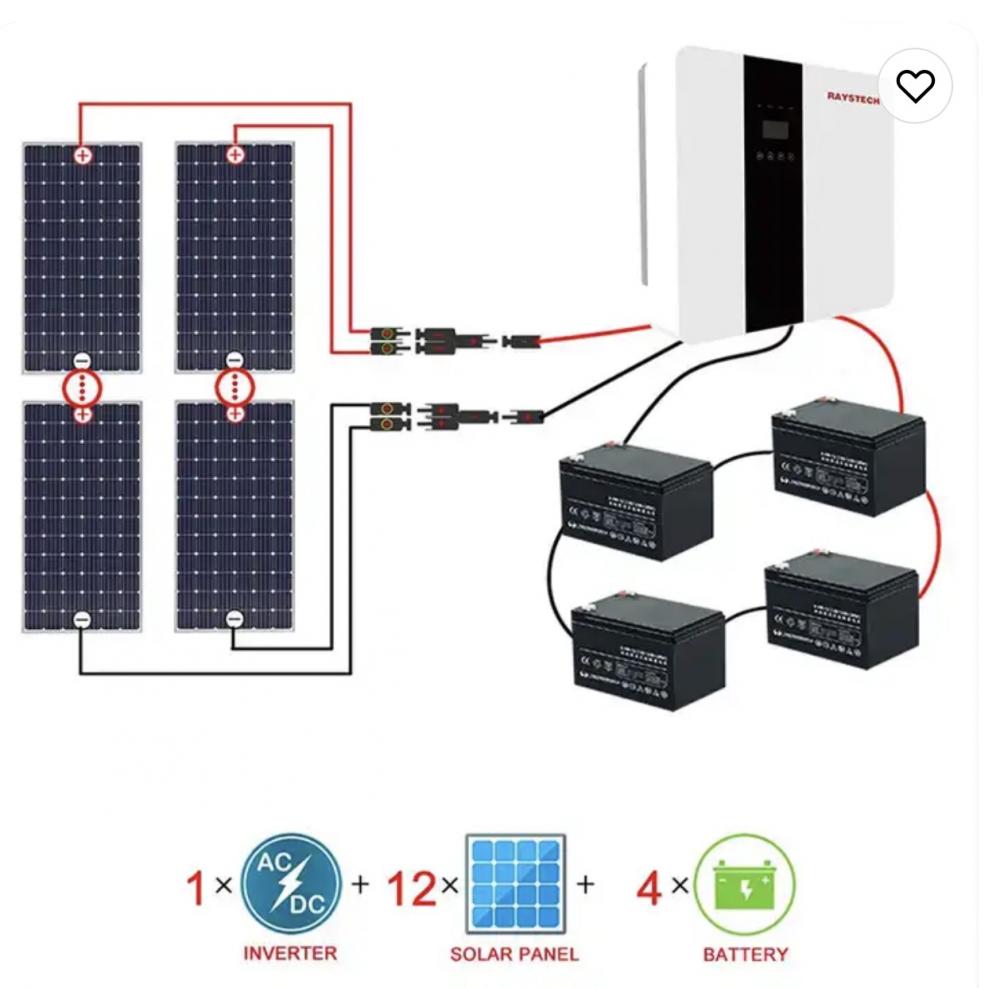

Solar Engergy System,Gird Solar Power System,Pv System For Carport,Energy System Off Grid Solar System
PLIER(Suzhou) Photovoltaic Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.pliersolar.com

