Photovoltaic power generation is a technology that directly converts sunlight into electricity using the photovoltaic effect of semiconductor materials. It typically consists of three main components: solar panels (or modules), a controller, and an inverter. These components are made up of various electronic parts. Solar cells are connected in series and packaged to form large-area solar modules, which are then combined with other system components to create a complete photovoltaic power generation system.
The core principle of photovoltaic power generation lies in the photoelectric effect of semiconductors. When photons from sunlight strike a metal surface, they can be absorbed by electrons within the material. If the energy of the photon is sufficient, it can enable an electron to overcome the binding force of the metal and escape as a photoelectron. In the case of silicon, which has four outer electrons, doping with elements like phosphorus (which has five outer electrons) creates N-type semiconductors, while doping with boron (which has three outer electrons) creates P-type semiconductors. When P-type and N-type materials are joined, a potential difference forms at their junction, creating a solar cell. When sunlight hits this P-N junction, electrons move from the N-side to the P-side, and holes move in the opposite direction, generating an electric current.
The photoelectric effect refers to the phenomenon where light induces a voltage between different regions of a semiconductor or between a semiconductor and a metal. This process involves two key steps: first, converting photons into electrons, thus transforming light energy into electrical energy; second, creating a voltage that allows for the flow of current.
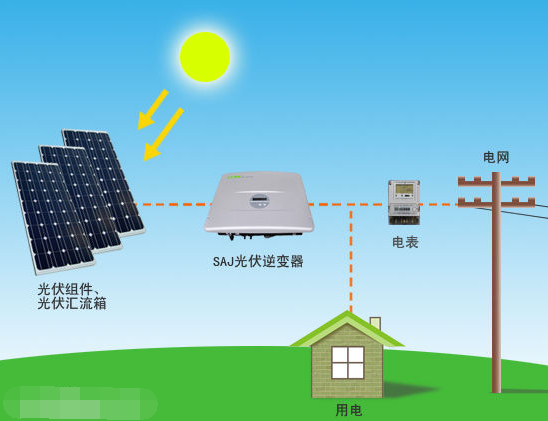
**Photovoltaic Power Generation Schematic**
After the polycrystalline silicon is grown into ingots, cut into wafers, and processed, a P-N junction is formed by doping the wafer with small amounts of boron or phosphorus. Then, silver paste is screen-printed onto the wafer to create a grid pattern, which is sintered to form the back electrode. An anti-reflective coating is applied to the front surface, and the completed cell is assembled into a module. These modules are then combined into larger arrays to form a complete circuit board.
Typically, the module is framed with aluminum, covered with glass on the front, and mounted with electrodes on the back. With additional components such as inverters and mounting structures, a full photovoltaic power generation system can be established. To convert DC power into AC for household use, an inverter is required. The generated electricity can either be stored in batteries or fed into the power grid. Approximately 50% of the total system cost comes from the solar modules, while the remaining 50% covers inverters, installation, and other auxiliary components.
**Does the home photovoltaic power station have radiation?**
A residential photovoltaic system includes photovoltaic modules, inverters, mounting structures, and cables. Photovoltaic power generation directly converts sunlight into direct current (DC) through semiconductor properties, and then uses an inverter to convert DC into alternating current (AC) for use. Since there are no chemical reactions or nuclear processes involved, photovoltaic systems do not emit harmful short-wave radiation.
Therefore, photovoltaic power generation is clean, non-polluting, and non-radiative, making it a sustainable and environmentally friendly energy source.

**Is it harmful to the body?**
Since photovoltaic modules do not emit radiation, they can reflect some harmful ultraviolet (UV) rays from the sun. This means that instead of being harmful, they actually help protect against UV exposure. Additionally, using photovoltaics reduces reliance on fossil fuels, which helps decrease pollution. For example, generating 1 kWh of solar power saves about 0.4 kg of standard coal and reduces emissions of carbon dust, carbon dioxide, sulfur dioxide, and nitrogen oxides. As a result, air quality improves, and smog decreases, offering significant environmental benefits.

**Will the roof be crushed?**
Most residential roofs can support up to 200 kg per square meter. Modern polycrystalline silicon photovoltaic modules weigh around 30 kg per square meter, so the added load is well within safe limits. During installation, engineers carefully consider factors such as roof load capacity, wind resistance, snow load, and seismic stability. Therefore, installing a rooftop photovoltaic system does not pose any structural risk to the building.

**Advantages and Disadvantages of Rural Rooftop Photovoltaic Power Generation**
In China, the development of distributed photovoltaics has been supported by national policies. In 2012, State Grid issued guidelines for grid-connected services for distributed photovoltaic systems. In 2013, China Southern Power Grid also released supporting policies. These measures helped open up the market for rooftop photovoltaic projects, leading to widespread adoption. However, early challenges included unclear grid connection rules, delayed subsidies, and unclear tax policies.
In 2013, the Ministry of Finance and State Administration of Taxation issued temporary tax exemptions for small enterprises. In 2014, the State Administration of Taxation provided guidance on billing and tax issues for distributed photovoltaic projects. As a result, homeowners could benefit from both grid-tied electricity prices and government subsidies, significantly improving the return on investment.
**Advantages of Home Photovoltaic Power Stations**
In China, rooftop photovoltaic installations offer quick results. A typical home PV system can be applied for in just 10 working days, installed in under 3 days, and connected to the grid in 7 days. The entire process can be completed in as little as 15 days. Subsidies are usually paid within three months.
**Small Investment**
For urban homes, a 5–8 kWp system is common, costing between 60,000 and 100,000 yuan. For rural homes, a smaller 3–5 kWp system can be installed for around 50,000 yuan, providing long-term savings and environmental benefits.
Vacuum Furnace Insulation Board
Vacuum Furnace Insulation Board,Carbon Fiber Surface Felt,Vacuum Furnace Insulation Barrel,High Pressure Carbon Fiber Insulation Material
HuNan MTR New Material Technology Co.,Ltd , https://www.hnmtr.com