Compare ipv4_ipv6 with ipv9
You might have heard of IP, but have you ever come across "IPv4" or "IPv6"? Chances are you know what they mean. But what about "IPv9"? Well, I didn't know much about it either. After doing some research online, I finally got a clearer picture and I'm excited to share this information with you.
IPv4 and IPv6 are the two main protocol families that currently power the global Internet. The original TCP/IP protocol used 32-bit addresses, which meant only around 4.3 billion unique IP addresses could exist. As the Internet grew rapidly, the demand for more addresses increased, leading to a shortage of IPv4 addresses. This is why we now talk about IPv4, IPv6, and even mention IPv9 in some discussions.
IPv4 and IPv6 Addresses Are Running OutAccording to various reports, the global IPv4 address pool was expected to be exhausted by 2010. In contrast, IPv6 uses a 128-bit address space, offering an almost unlimited number of addresses. Even when conservatively estimated, IPv6 can allocate over 1,000 addresses per square meter of the Earth's surface. This makes it a far more scalable solution for the future of the Internet.
When designing IPv6, developers aimed not only to solve the address shortage issue but also to improve several aspects that were lacking in IPv4. These include end-to-end connectivity, quality of service (QoS), security, multicast support, mobility, and plug-and-play capabilities. 2011 marked a turning point as the last IPv4 addresses were distributed worldwide, signaling the start of a real transition to IPv6.
What Is IPv9?Now, let’s talk about IPv9. A few years ago, it was promoted as a way to maintain China’s network sovereignty. However, it has since fallen out of the spotlight. The inventor, Xie Jianping, along with his team, has kept the technical details of IPv9 as commercial secrets. Recently, some domestic users have started talking about IPv9 again, claiming it’s a simpler version of the protocol. One of its key features is using decimal numbers for URL encoding, allowing users to type something like "12345" instead of a traditional domain name.

How Does IPv6 Compare to IPv4?
IPv6 offers a significantly larger address space. While IPv4 uses 32-bit addresses, giving us around 4.3 billion addresses, IPv6 uses 128 bits, providing a massive number of possible addresses—about 3.4 x 10^38. This expansion helps reduce the burden on routing tables. IPv6 addresses are allocated in a clustered manner, which allows routers to manage large subnets with fewer entries, improving efficiency and speed.
IPv6 also improves support for multicast and flow control, making it ideal for multimedia applications and better QoS. It includes built-in auto-configuration, simplifying network management. Additionally, IPv6 enhances security by supporting encryption and packet authentication at the network layer, making it more secure than IPv4.
China's Own IPv9 Faces Challenges
Reports suggest that China's three major telecom operators are pushing for the development of IPv6. Duan Xiaodong from China Mobile’s Network Technology Research Institute emphasized the need for devices and terminals to support IPv6. This aligns with previous statements that mobile devices lack sufficient IPv6 support and require urgent improvements.
Zeng Gaofei noted that while there are discussions around IPv9, it remains largely theoretical and hasn’t been officially announced or approved. He also pointed out that current mobile TD terminals still lack IPv6 compatibility, and chip development is behind. China Mobile’s approach involves requiring manufacturers to adopt foreign technology, which could increase costs and slow down progress.
As a result, Chinese companies still struggle to develop their own solutions, relying heavily on external technologies. The high cost of implementation deters manufacturers from producing IPv6-enabled devices, and without a clear market demand, it’s hard for companies to justify the investment. This creates a challenge for China’s push toward IPv6 adoption.
Inversion DC - AC Power Supplies
IPS series DC - AC inversion power supplies are new generation of power dedicated AC Power Supplies for power system applications. It is mainly designed and manufactured according to the characteristics and requirements of power system.
This series of DC - AC power supplies can be divided into single-phase and three-phase AC power supplies according to the difference in the number of output phases. The output power of single-phase DC to AC power supplies ranges from 1KVA to 10KVA, and the output power of three-phase DC to AC power supplies ranges from 15KVA to 60KVA. The output voltage is divided into single-phase 220Vac and three-phase 380Vac with 50Hz fixed frequency output.
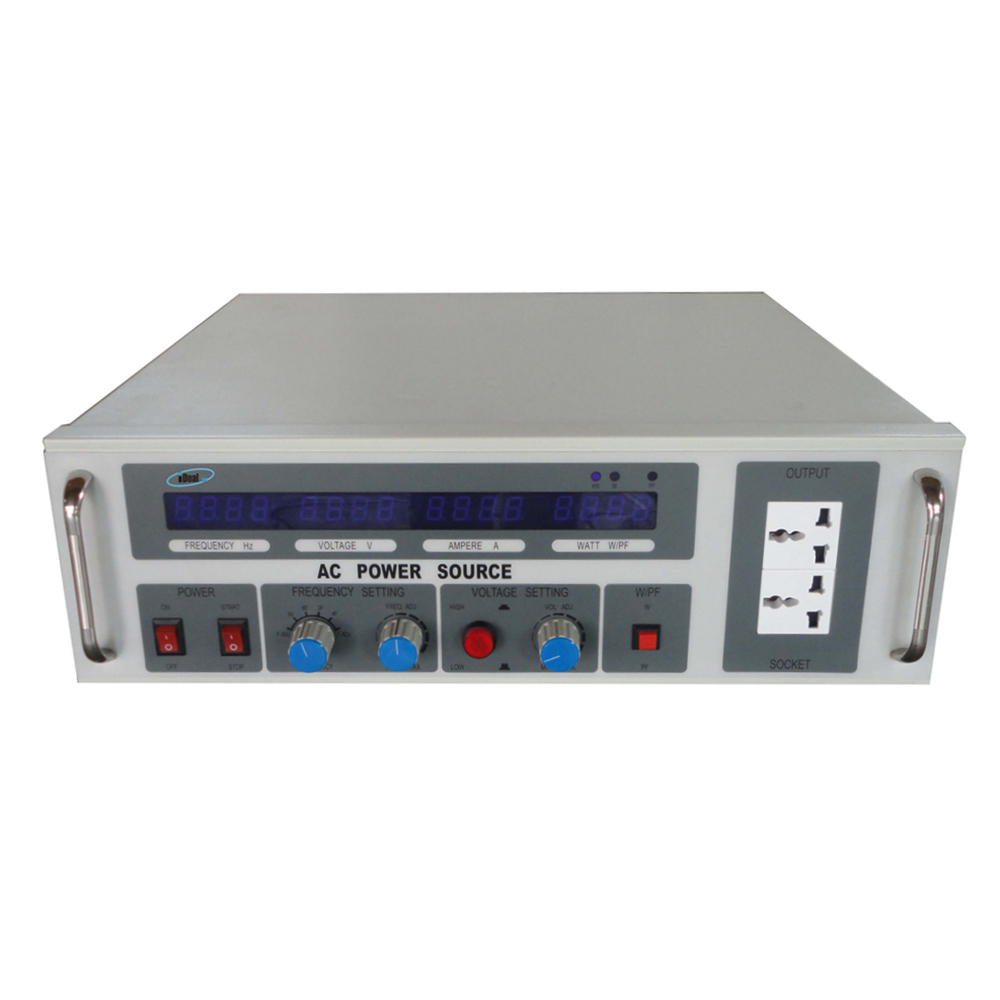
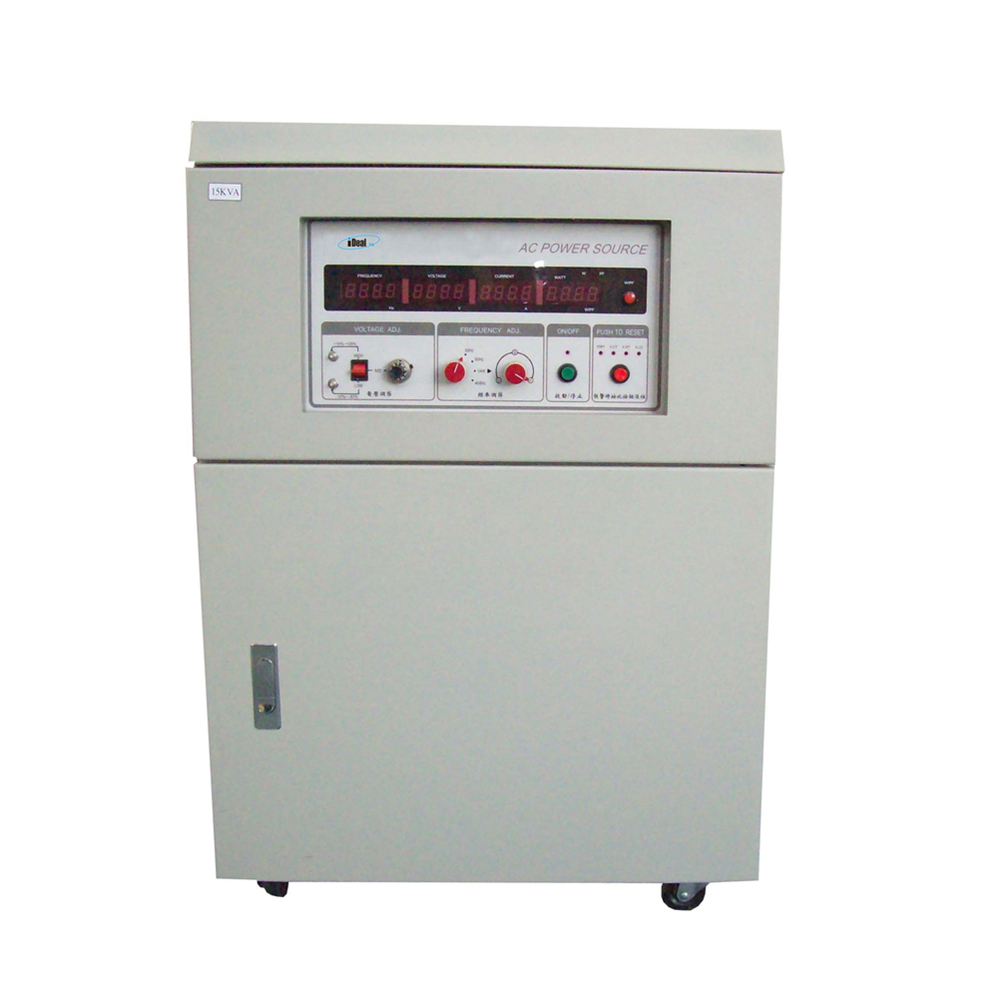


Now, the inversion AC power supplies are widely used in power system communication, carrier, monitoring, relay protection and humidity lighting, and can also provide uninterrupted power for AC lubricating pumps, AC fans, and water pumps in power plants. And it is widely used in various fields such as aerospace, financial system, office automation control, medical and health, military scientific research and so on.
DC - AC Power Supplies, AC Inversion Power Supplies, Inversion AC Power Supplies, DC to AC Power Supplies, Inversion AC Power Source
Yangzhou IdealTek Electronics Co., Ltd. , https://www.idealtekpower.com